
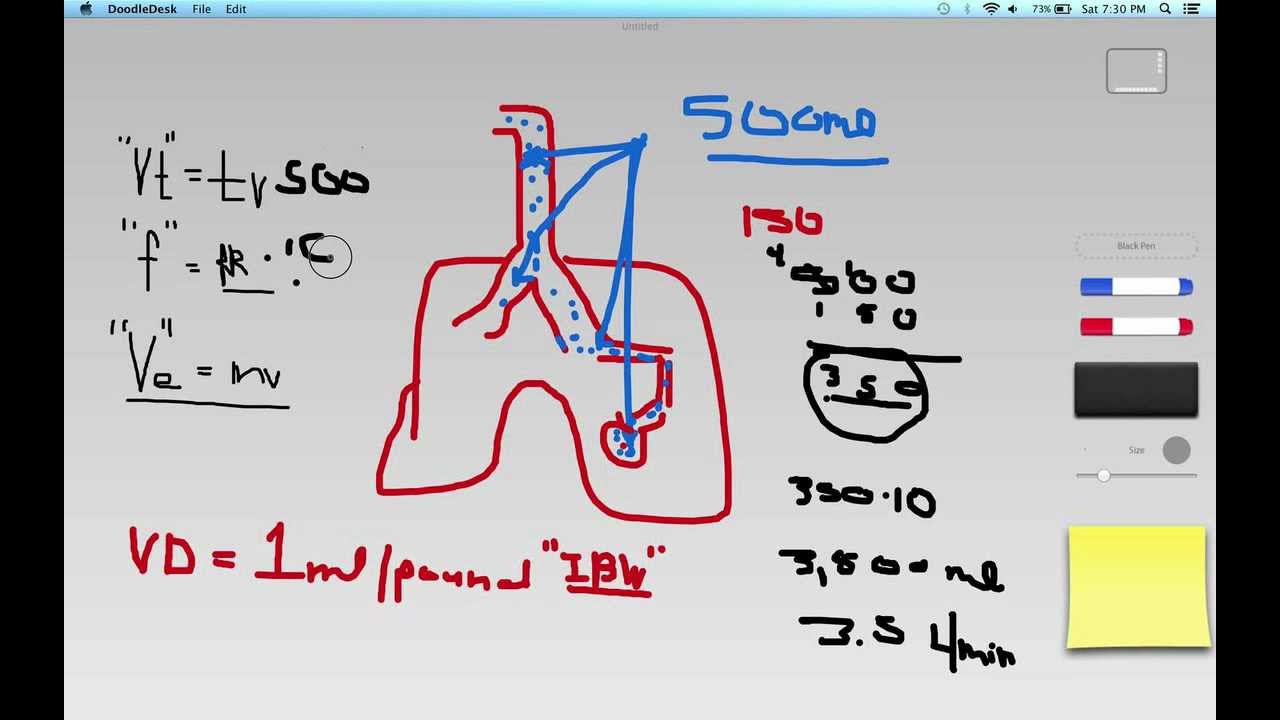
#CALCULATING TIDAL VOLUME FULL#
See /license for the full LOINC copyright and license. and the Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC) Committee. To the extent included herein, the LOINC table and LOINC codes are copyright © 1995-2023, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. CodeSystem lookup https: ///CodeSystem/$lookup?system=http: //&code=60869-5 LOINC CopyrightĬopyright © 2023 Regenstrief Institute, Inc.
See the LOINC Terminology Service documentation for more information. Below is a sample of the possible capabilities.
#CALCULATING TIDAL VOLUME FREE#
Requests to this service require a free LOINC username and password. LOINC Terminology Service (API) using HL7 ® FHIR ® Get Info The perceived complexity of calculating an ideal body weight (IBW)-based tidal volume (Vt) may contribute to this disparity. Spazio morto fisiologico^con respiratore: Vol: Pt: Apparato respiratorio: Qn: Synonyms: Gestione ventilazione polmonare Punto nel tempo (episodio) Volume Vd=*Vt Vd=dead space volume, Vt=tidal volume, PaCO2=arterial partial pressure of CO2, PeCO2=partial pressure of CO2 in expired gas Language Variants Get Info TagĮspacio muerto fisiológico ^ en el ventilador: Volumen: Punto temporal: Sistema respiratorio: Cuantitativo: Urn:iso:std:iso:11073:10101 (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)īasic Attributes Class PULM Type Clinical First Released Version 2.54 Last Updated Version 2.70 Order vs.
#CALCULATING TIDAL VOLUME CODE#
Source: Regenstrief LOINC Fully-Specified Name Component Physiological dead space^on ventilator Property Vol Time Pt System Respiratory system Scale Qn Method Additional Names Short Name Phys dead space on vent Vol Respiratory Related Codes Code System PeCO2 is the partial pressure of CO2 in expired gas PaCO2 is arterial partial pressure of CO2 Physiological dead space can be calculated using Bohr's equation: Alveolar dead space is the volume of alveoli that are ventilated but not perfused (or underperfused), and anatomical dead space is the volume of the respiratory system from the nose and mouth to the level of the distal airways at which gas exchange begins to take place. It includes both alveolar and anatomical dead space. The accuracy of the formula derived by Drorbaugh and Fenn (Pediatrics 16: 81-86, 1955) for calculating tidal volume (VT) from the phasic pressure change measured when an animal breathes in a closed chamber has recently been challenged. LP101939-9 Physiological dead space The physiological dead space is the volume of gas in the respiratory system that is not involved in respiratory gas exchange.

To facilitate its use, TN was measured in rat, rabbit, cat, man, and infant pigtail monkey.60869-5 Physiological dead space Respiratory system -on ventilator Active Part Description
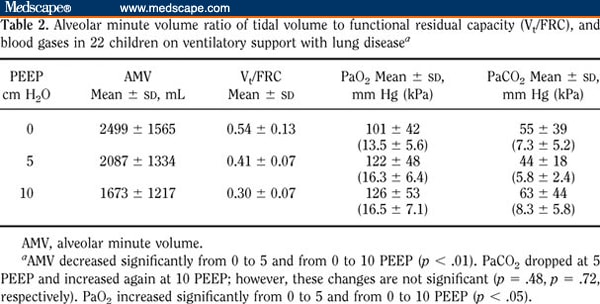
It requires knowledge of TN and TI/Ttot and reduces the error between experiments to under 20% and within each experiment to about 5%. A factor is derived for retrospectively correcting VT estimated by the Drorbaugh-Fenn formula. TN was varied from ambient to body temperature by passing a variable current through the pneumotachograph heater TI/Ttot was varied by changing FICO2 and by selecting different rats. To test their theory, I measured VT in anesthetized rats by the barometric technique and by conventional pneumotachography simultaneously. 32: 105-120, 1978) argue that the formula may underestimate VT by up to 30% and predict that the error increases as the ratio of inspiratory duration (TI) to total breath duration (Ttot) increases, and as the expired temperature at the nares (TN) increases.

The accuracy of the formula derived by Drorbaugh and Fenn (Pediatrics 16: 81-86, 1955) for calculating tidal volume (VT) from the phasic pressure change measured when an animal breathes in a closed chamber has recently been challenged.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
